 This is the second part of a five part tutorial that will show you how to install a full featured email server on your Raspberry Pi. This tutorial covers Dovecot, which provides SASL authentication and IMAP capabilities.
This is the second part of a five part tutorial that will show you how to install a full featured email server on your Raspberry Pi. This tutorial covers Dovecot, which provides SASL authentication and IMAP capabilities.
The parts are:
The Introduction & Contents Page (read first)
Raspberry Pi Email Server Part 1: Postfix
Raspberry Pi Email Server Part 2: Dovecot
Raspberry Pi Email Server Part 3: Squirrelmail
Raspberry Pi Email Server Part 4: Spam Detection with Spamassassin
Raspberry Pi Email Server Part 5: Spam Sorting with LMTP & Sieve
Fixing the errors that appeared during dovecot installation
In part 1, when you installed Dovecot I mentioned that you might see some errors like this:
Creating config file /etc/dovecot/conf.d/20-imap.conf with new version [....] Restarting IMAP/POP3 mail server: dovecotError: socket() failed: Address family not supported by protocol Error: service(imap-login): listen(::, 143) failed: Address family not supported by protocol Error: socket() failed: Address family not supported by protocol Error: service(imap-login): listen(::, 993) failed: Address family not supported by protocol Fatal: Failed to start listeners failed! invoke-rc.d: initscript dovecot, action "restart" failed. dpkg: error processing dovecot-imapd (--configure): subprocess installed post-installation script returned error exit status 1 Setting up dovecot-ldap (1:2.1.7-7) ...
These errors are caused by the lack of IPv6 support, which I mentioned in the previous tutorial. To remove the errors, open the main dovecot configuration file (/etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf) and find this line:
listen = *, ::
And change it to:
listen = *
The * means “all IPv4 addresses”, the :: means “all IPv6 addresses”. Now restart Dovecot, and you shouldn’t get any errors:
sudo service dovecot restart
Note: since I wrote this tutorial, there have been a few small changes to the default configuration file - you may find that the line is commented (with a # at the start of the line). If so, remember to uncomment it when you make your changes!
Tell Dovecot where your Mailbox is
Open /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf and find this line:
mail_location = mbox:~/mail:INBOX=/var/mail/%u
Change it to this:
mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir
Instruct Postfix to use Dovecot SASL
Now we need to tell Postfix that we would like to use Dovecot for SASL authentication. Open /etc/postfix/main.cf and add these lines:
smtpd_sasl_type = dovecot smtpd_sasl_path = private/auth smtpd_sasl_auth_enable = yes
Now tell Dovecot to listen for SASL authentication requests from Postfix. Open /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-master.conf and comment out the current block that begins with service auth (place a # at the start of each line). Replace it with this:
service auth {
unix_listener /var/spool/postfix/private/auth {
mode = 0660
user = postfix
group = postfix
}
}
Now you want to enable plain text logins. Do it by adding these two lines to /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf. Make sure they are not already present in the file, or your settings may be overwritten with the default ones if the default is declared later in the file than the lines you add. If the parameters are already present, you can either modify the existing lines or comment them out and add these new ones:
disable_plaintext_auth = no auth_mechanisms = plain login
Note that although the logins are in plain text, we will be setting Postfix up later so that it only allows you to use plaintext logins from within SSL/TLS. This means that your login and password will sent in an encrypted session - you wouldn't see them in plain text if you used a packet sniffer, for example. For now, we’re allowing unencrypted plain text logins so that we can test logging in with Telnet. Since the connection is local (from the Pi to the Pi), your password isn’t being sent over any insecure networks so this is fine.
Testing SASL
Creating a new user for testing purposes is a good idea. Let’s call this temporary user testmail and give it the password test1234 Use this command to add the user, and follow the prompts including setting a password.
sudo adduser testmail
Now restart Postfix and Dovecot:
sudo service postfix restart sudo service dovecot restart
We’re now going to try and send an email after authenticating with SASL. The server is expecting to see a base64 encoded version of your username and password, so we have to convert it first. There are three ways of doing this, so I've given examples below using the testmail username and test1234 password:
#Method No.1
echo -ne '\000testmail\000test1234' | openssl base64
#Method No.2
perl -MMIME::Base64 -e 'print encode_base64("\0testmail\0test1234");'
#Method No.3
printf '\0%s\0%s' 'testmail' 'test1234' | openssl base64
I have discovered that if your password starts with a number, methods 1 and 2 don’t work. Assuming the username and password are testmail and test1234, the commands produce this:
AHRlc3RtYWlsAHRlc3QxMjM0
WARNING: If you’re having problems with authentication and you paste examples to forums or mailing lists, be aware that it is really easy to convert this back into your username and password (hence the creation of a test user). If you're using your real username and password to test, redact it before posting! Now, still logged into the Pi via SSH, you can telnet port 25 to test whether or not SASL is working. There’s only one extra step, which is the AUTH PLAIN command that comes after ehlo but before mail from. For testing, the permit_mynetworks parameter should be commented out under your postfix smtpd_recipient_restrictions block in /etc/postfix/main.cf. If you’re following on from Raspberry Pi Email Server Part 1: Postfix then this should already be the case. If you have to change it, remember to reload postfix (sudo service postfix reload) after you change the value. Here’s an example:
telnet localhost 25 Trying 127.0.0.1... Connected to localhost. Escape character is '^]'. 220 samhobbs ESMTP Postfix (Debian/GNU) ehlo facebook.com 250-samhobbs 250-PIPELINING 250-SIZE 10240000 250-VRFY 250-ETRN 250-STARTTLS 250-AUTH PLAIN LOGIN 250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES 250-8BITMIME 250 DSN AUTH PLAIN AHRlc3RtYWlsAHRlc3QxMjM0 235 2.7.0 Authentication successful mail from:testmail 250 2.1.0 Ok rcpt to:me@externalemail.com 250 2.1.5 Ok data 354 End data with. Subject: This is my first email that has been authenticated with Dovecot SASL Woop woop . 250 2.0.0 Ok: queued as B87133F768 quit 221 2.0.0 Bye Connection closed by foreign host.
Now try again but enter the username/password incorrectly (base64 encode something random) – you should get an error message and the email won’t send. If everything went to plan, then SASL is working properly! You can now uncomment permit_mynetworks again.
Separating Incoming email (unauthenticated) from Outgoing Email (SASL authenticated)
It’s probably a good idea to have a dedicated port for sending outgoing email…here’s why: Port 25 doesn’t require (but does offer) SSL/TLS encryption. If you mess up configuring your mail client you could end up letting it authenticate with SASL over insecure connections. Using a different port that only accepts SSL/TLS connections removes the risk that a poorly configured email client could be sending your password unencrypted over dodgy networks. There are two ports you can use for this:
- 465: SMTP over SSL
- 587: Email submission
587 is the “official” port for email clients (like K9 mail, Thunderbird and Outlook) to use when submitting messages to the Mail Submission Agent (your email server) – the submission may be encrypted or unencrypted depending on the server configuration. 465 was a port that was assigned for SMTP with SSL/TLS before the STARTTLS protocol was introduced, back in the days when you chose your port and that decided on the type of connection you were going to get (encrypted or unencrypted). STARTTLS changed things because it allows you to connect with an unencrypted connection (like the one you get with Telnet), and then upgrade to an encrypted connection without changing port… so when STARTTLS was introduced, SMTPS on port 465 was removed from the standard because you could do the same thing with a single port (25). However, I think there is some value in specifying a port for submission that only accepts SSL/TLS encrypted connections, and won’t work if the connection isn’t encrypted. This means that if you misconfigure your email client it just won’t work, instead of working and sending your password in an unencrypted format. So, anyway… Here’s how to set up Postfix to listen on port 465 for encrypted connections. The first step is telling Postfix to listen on port 465, so open /etc/postfix/master.cf and uncomment the line:
smtps inet n - - - - smtpd
Now restart Postfix:
sudo service postfix restart
Test whether Postfix is listening on port 465:
telnet localhost 465 Trying 127.0.0.1... Connected to localhost. Escape character is '^]'. 220 samhobbs.co.uk ESMTP Postfix (Debian/GNU) ehlo samhobbs.co.uk 250-samhobbs 250-PIPELINING 250-SIZE 10240000 250-VRFY 250-ETRN 250-STARTTLS 250-AUTH PLAIN LOGIN 250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES 250-8BITMIME 250 DSN quit 221 2.0.0 Bye Connection closed by foreign host.
OK, so now it’s listening on the right port, but it’s allowing unencrypted connections. Here’s how you force TLS on port 465: open /etc/postfix/master.cf and find the line you uncommented earlier. Below it are some options, you want to edit them so that they look like this (i.e. uncomment lines 2 and 3):
smtps inet n - - - - smtpd -o syslog_name=postfix/smtps -o smtpd_tls_wrappermode=yes
Line 3 is forcing TLS on port 465, and line 2 means that connections to port 465 have a different label in the logs, which can be useful for debugging.
sudo service postfix restart
Now try connecting with Telnet again… you should be able to establish a connection, but not receive any prompts from the server:
telnet localhost 465 Trying 127.0.0.1... Connected to localhost. Escape character is '^]'. exit exit Connection closed by foreign host.
Now try openssl:
openssl s_client -connect localhost:465 -quiet depth=0 CN = samhobbs verify error:num=18:self signed certificate verify return:1 depth=0 CN = samhobbs verify return:1 220 samhobbs.co.uk ESMTP Postfix (Debian/GNU) quit 221 2.0.0 Bye
Good: we are able to start a TLS encrypted connection. We got some errors because the certificate is self-signed (it's not signed by a certificate that is in the trusted root store on the server) but this is OK because we're just using the certificate for testing for now. When you come back later to set up a proper certificate, you can use this command to verify it. The -CApath option tells openssl where the trusted certificates are stored on your system:
openssl s_client -connect localhost:465 -quiet -CApath /etc/ssl/certs
Successful validation looks something like this:
sam@samhobbs:~$ openssl s_client -connect localhost:465 -quiet -CApath /etc/ssl/certs depth=3 C = SE, O = AddTrust AB, OU = AddTrust External TTP Network, CN = AddTrust External CA Root verify return:1 depth=2 C = GB, ST = Greater Manchester, L = Salford, O = COMODO CA Limited, CN = COMODO RSA Certification Authority verify return:1 depth=1 C = GB, ST = Greater Manchester, L = Salford, O = COMODO CA Limited, CN = COMODO RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA verify return:1 depth=0 OU = Domain Control Validated, OU = PositiveSSL, CN = samhobbs.co.uk verify return:1 220 samhobbs.co.uk ESMTP Postfix (Ubuntu) quit 221 2.0.0 Bye
There are a couple more changes we want to make here: first, tell Postfix to only advertise SASL authentication over encrypted connections (so that you don’t accidentally send your password in the clear). Open /etc/postfix/main.cf and add this line:
smtpd_tls_auth_only = yes
sudo service postfix reload
Now connect to port 25 and you shouldn’t see AUTH advertised:
telnet localhost 25 Trying 127.0.0.1... Connected to localhost. Escape character is '^]'. 220 samhobbs.co.uk ESMTP Postfix (Debian/GNU) ehlo samhobbs.co.uk 250-samhobbs.co.uk 250-PIPELINING 250-SIZE 10240000 250-VRFY 250-ETRN 250-STARTTLS 250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES 250-8BITMIME 250 DSN
Lastly, we want to override the smtp_recipient_restrictions for port 465 so that it doesn't accept incoming messages from unauthenticated users. At first, I didn't make this change and I noticed that some spam emails were coming in on port 465 and bypassing my spam filter, which I configured to scan all incoming email on port 25, but not 465 because I only expected it to be used for outgoing email. We can do this by overriding the smtp_recipient_restrictions list for port 465 in /etc/postfix/master.cf. Open master.cf and find the smtps line. Add a new recipient restrictions list option like this:
smtps inet n - - - - smtpd -o syslog_name=postfix/smtps -o smtpd_tls_wrappermode=yes -o smtpd_recipient_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject
Now reload postfix:
sudo service postfix reload
Perfect! Postfix configuration is now complete.
Testing IMAP
There are two main protocols for fetching mail: POP and IMAP. The main difference between them is what they do with emails when they collect them: a POP client will fetch email from your server and remove it from the server when it’s done. This is inconvenient if you want to connect with two or more devices (like a phone and a computer) and have complete copies of all your emails on both. IMAP, on the other hand, makes a copy of the emails on the server and leaves the originals there. For this reason, I think IMAP is much more useful than POP and I didn’t even bother to set up POP on my server. We can now test the IMAP server with Telnet in a similar way to SMTP & SASL testing earlier. This time, we’ll be using port 143, the standard port for IMAP. The stages are:
- establish a connection with
telnet localhost 143 - log in with
a login "USERNAME" "PASSWORD"" (not base64 encoded this time) - select inbox to see messages inside
b select inbox - logout with
c logout
In case you're wondering, the "a b c" thing is done because a client can send multiple commands to the server at once, and they might not come back in the same order depending on what they are. So, the responses have the same letter as the commands they are responding to so that the client doesn't get muddled. Here’s an example, using the testmail user we created earlier:
telnet localhost 143 Trying 127.0.0.1... Connected to localhost. Escape character is '^]'. * OK [CAPABILITY IMAP4rev1 LITERAL+ SASL-IR LOGIN-REFERRALS ID ENABLE IDLE STARTTLS AUTH=PLAIN AUTH=LOGIN] Dovecot ready. a login "testmail" "test1234" a OK [CAPABILITY IMAP4rev1 LITERAL+ SASL-IR LOGIN-REFERRALS ID ENABLE IDLE SORT SORT=DISPLAY THREAD=REFERENCES THREAD=REFS MULTIAPPEND UNSELECT CHILDREN NAMESPACE UIDPLUS LIST-EXTENDED I18NLEVEL=1 CONDSTORE QRESYNC ESEARCH ESORT SEARCHRES WITHIN CONTEXT=SEARCH LIST-STATUS SPECIAL-USE] Logged in b select inbox * FLAGS (\Answered \Flagged \Deleted \Seen \Draft) * OK [PERMANENTFLAGS (\Answered \Flagged \Deleted \Seen \Draft \*)] Flags permitted. * 1 EXISTS * 0 RECENT * OK [UNSEEN 1] First unseen. * OK [UIDVALIDITY 1385217480] UIDs valid * OK [UIDNEXT 2] Predicted next UID * OK [NOMODSEQ] No permanent modsequences b OK [READ-WRITE] Select completed. c logout * BYE Logging out c OK Logout completed. Connection closed by foreign host.
Adding TLS support
Now that we know IMAP is working, we need to enable IMAPS (imap with SSL/TLS). The standard port for this is 993. Many other tutorials that were written for older versions of dovecot will tell you to do this in different ways that won’t work, I tried 3 different methods before I ended up with a working one. First, edit /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-master.conf, find the “service imap-login” block and uncomment the port and SSL lines so that it looks like this:
service imap-login {
inet_listener imap {
port = 143
}
inet_listener imaps {
port = 993
ssl = yes
}
}
Edit 14/10/2015: the default dovecot configuration files changed recently after Jessie became the new stable distribution of Debian, which caused some users problems; TLS on port 993 used to be enabled by default but now it isn't. We need to re-enable it. In /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-ssl.conf, find ssl = no and change it to:
ssl = yes
There have been some security vulnerabilities discovered in older versions of the SSL protocol in recent times. SSLv2 is disabled by default, but it doesn't harm to explicitly disable it again. SSLv3 is vulnerable to an attack called POODLE, so we will disable it too. In the same file, find the ssl_protocols parameter line, uncomment it and add !SSLv3 to the end, like this:
ssl_protocols = !SSLv2 !SSLv3
Edit 02/09/2017: if you're using Debian Stretch or later, or one of its derivatives, then you will need to edit that line to match the following. The SSLv2 option is no longer recognised as an option for ssl_protocols because it has been removed entirely:
ssl_protocols = !SSLv3
For some bizarre reason, the Dovecot package for Raspberry Pi (and possibly newer versions of Ubuntu) does not create a self-signed certificate during installation like it used to. So, we have to create one manually. If you look in /usr/share/dovecot/ you will find the script that used to be used to generate the certificate; we can use it ourselves to simplify the process. The script is located at /usr/share/dovecot/mkcert.sh and looks like this:
#!/bin/sh
# Generates a self-signed certificate.
# Edit dovecot-openssl.cnf before running this.
OPENSSL=${OPENSSL-openssl}
SSLDIR=${SSLDIR-/etc/ssl}
OPENSSLCONFIG=${OPENSSLCONFIG-dovecot-openssl.cnf}
CERTDIR=/etc/dovecot
KEYDIR=/etc/dovecot/private
CERTFILE=$CERTDIR/dovecot.pem
KEYFILE=$KEYDIR/dovecot.pem
if [ ! -d $CERTDIR ]; then
echo "$SSLDIR/certs directory doesn't exist"
exit 1
fi
if [ ! -d $KEYDIR ]; then
echo "$SSLDIR/private directory doesn't exist"
exit 1
fi
if [ -f $CERTFILE ]; then
echo "$CERTFILE already exists, won't overwrite"
exit 1
fi
if [ -f $KEYFILE ]; then
echo "$KEYFILE already exists, won't overwrite"
exit 1
fi
$OPENSSL req -new -x509 -nodes -config $OPENSSLCONFIG -out $CERTFILE -keyout $KEYFILE -days 365 || exit 2
chmod 0600 $KEYFILE
echo
$OPENSSL x509 -subject -fingerprint -noout -in $CERTFILE || exit 2
If you were going to use this certificate for any significant length of time, it would be worth editing the parameters in the config file it uses (/usr/share/dovecot/dovecot-openssl.cnf) to set the proper common name and contact details on the certificate. However, I suggest you leave the defaults as they are, use this certificate just for testing, and then come back later and generate a new cert when everything is working (more on that later). You must be in the same folder as the configuration file when you run the script, or it will not find the config and the certificate generation will fail. The following two commands will change to the right folder and then execute the script:
cd /usr/share/dovecot sudo ./mkcert.sh
You should see a message "writing new private key to '/etc/dovecot/private/dovecot.pem'" and then some details about the certificate. Next, find the following two lines in /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-ssl.conf and uncomment them:
#ssl_cert = </etc/dovecot/dovecot.pem #ssl_key = </etc/dovecot/private/dovecot.pem
Now reload dovecot to apply the changes:
sudo service dovecot reload
Since IMAPS is a connection over SSL/TLS, we can’t use Telnet to test it. Instead, we use openssl to create a secure connection. There are two versions of the command, one will show you LOADS of information about the certificate used to encrypt the connection, and the other will suppress this info. I recommend trying the long version out of interest, but both will work the same for the test: For full information:
openssl s_client -connect localhost:993
For minimal information:
openssl s_client -connect localhost:993 -quiet
I won’t print the output of the first command, because it’s ridiculously long. Here’s an example of the second, including a login test:
admin@samhobbs /etc/dovecot/conf.d $ openssl s_client -connect localhost:993 -quiet depth=0 O = Dovecot mail server, OU = samhobbs, CN = samhobbs, emailAddress = root@samhobbs.co.uk verify error:num=18:self signed certificate verify return:1 depth=0 O = Dovecot mail server, OU = samhobbs, CN = samhobbs, emailAddress = root@samhobbs.co.uk verify return:1 * OK [CAPABILITY IMAP4rev1 LITERAL+ SASL-IR LOGIN-REFERRALS ID ENABLE IDLE AUTH=PLAIN AUTH=LOGIN] Dovecot ready. a login "testmail" "test1234" a OK [CAPABILITY IMAP4rev1 LITERAL+ SASL-IR LOGIN-REFERRALS ID ENABLE IDLE SORT SORT=DISPLAY THREAD=REFERENCES THREAD=REFS MULTIAPPEND UNSELECT CHILDREN NAMESPACE UIDPLUS LIST-EXTENDED I18NLEVEL=1 CONDSTORE QRESYNC ESEARCH ESORT SEARCHRES WITHIN CONTEXT=SEARCH LIST-STATUS SPECIAL-USE] Logged in b logout * BYE Logging out b OK Logout completed. Connection closed by foreign host.
Good stuff: SSL/TLS is working on port 993, and you can log in successfully. Note that by default Dovecot uses a “snakeoil” self-signed certificate. SSL/TLS certificates are used for two purposes: encryption and verification. The “snakeoil” certificate will encrypt your content but it won’t verify that you’re talking to your server – you could be talking to someone imitating your server (anyone can create a self-signed certificate claiming to be any website). If you’d like to get your certificate signed without forking out loads of money to a cert signing authority, I’d recommend CAcert. I've written a tutorial explaining how to generate your own cert and get it signed here. If you opt for a commercial certificate, you can use the CAcert tutorial to generate the certificate and then this tutorial will explain the differences in the installation/configuration of commercial certificates once you have it signed. If you're testing a proper certificate, use this command to tell openssl where the trusted root certificates are stored:
openssl s_client -connect localhost:993 -quiet -CApath /etc/ssl/certs
Tidying up and enabling WAN access
Before opening the ports on your router to the world, it’s a good idea to delete that test user because the password is so easy to guess.
sudo userdel testmail
Also, if you still use the "pi" login, for goodness' sake change the password from "raspberry"! You can do this using the passwd command when logged in as pi:
passwd
Or you can achieve the same thing when logged in as another user by using sudo to gain root privileges:
sudo passwd pi
Now you can open a few ports on your router’s firewall. Make sure your Pi has a static LAN IP address and then forward these ports from WAN to its LAN IP address:
- Port 25 for SMTP (used for receiving emails)
- Port 465 for secure SMTP (used for sending emails after SASL authentication)
- Port 993 for IMAPS (used to receive emails on your phone/tablet/computer)
Here’s an example on my router, running OpenWrt: 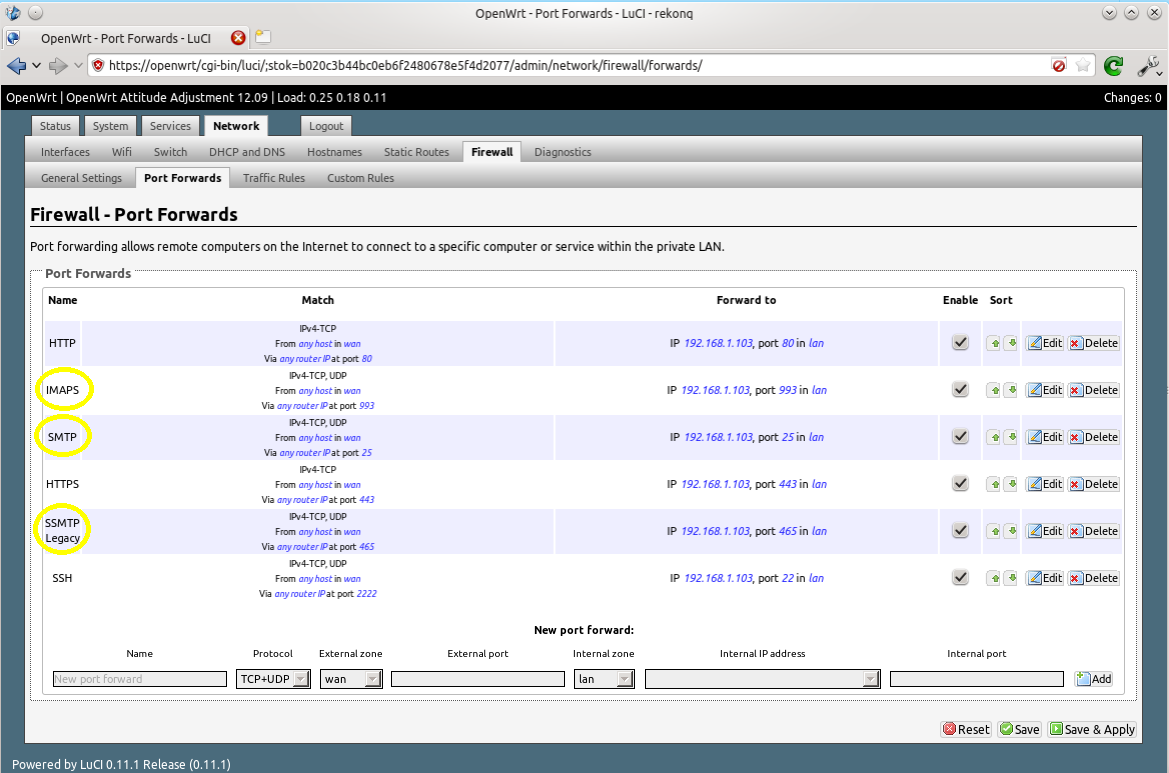
Setting up IMAP Email Clients
I’m now going to run through setting up IMAP email clients quickly, using K9 Mail on Android and Thunderbird on GNU/Linux as examples. The setup for Thunderbird on Windows and Mac OSX should be very similar. The basics are this:
- Select an IMAP connection
- Your login is your username only (omit @yourdomain.com), and you password is…your password!
- For incoming emails: select use SSL/TLS always and the program should automatically select port 993
- For outgoing emails: select SSL/TLS always. The program may suggest port 587, but you want port 465
K9 Mail
Open K9 Mail and select add new account. Type in your account information (you@yourdomain.com and password) and then select manual setup. Select IMAP and then enter your information as follows… Incoming email: 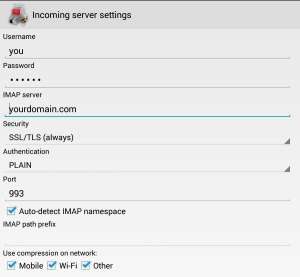 Outgoing email:
Outgoing email: 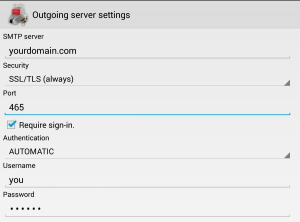
Thunderbird
Open Thunderbird, and then click Account Actions –> Add Mail Account. Fill in your password and email address, which is your username followed by your fully qualified domain name (FQDN), i.e. username@yourdomain.com: 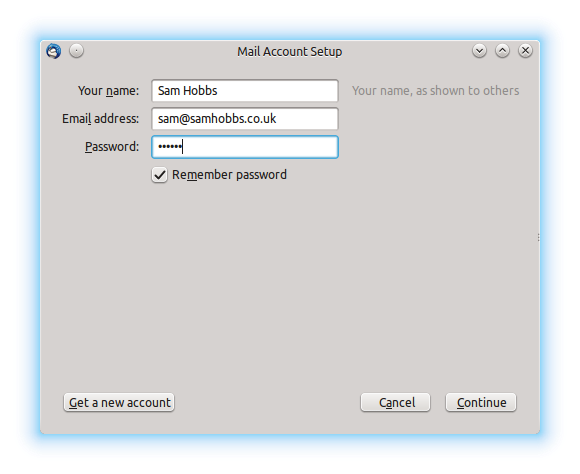 Thunderbird will try to auto-detect settings and fail. Don’t worry, this is normal. Select “manual config”:
Thunderbird will try to auto-detect settings and fail. Don’t worry, this is normal. Select “manual config”: 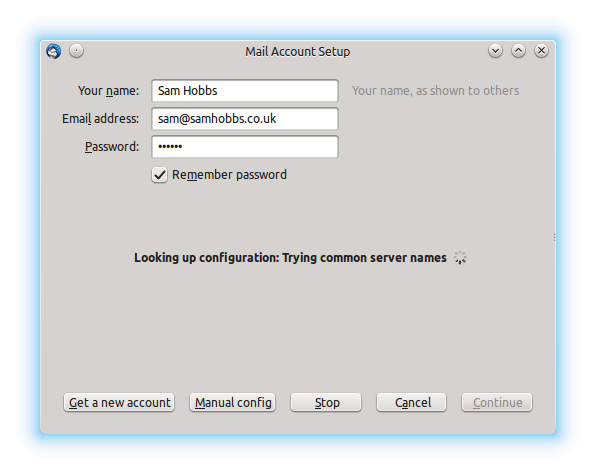 Now edit the settings as appropriate. I had to remove a period (.) from in front of my “server hostname”, and edit the SSL and Authentication settings. If you select “SSL/TLS” for both incoming and outgoing, ports 993 and 465 are automatically selected:
Now edit the settings as appropriate. I had to remove a period (.) from in front of my “server hostname”, and edit the SSL and Authentication settings. If you select “SSL/TLS” for both incoming and outgoing, ports 993 and 465 are automatically selected: 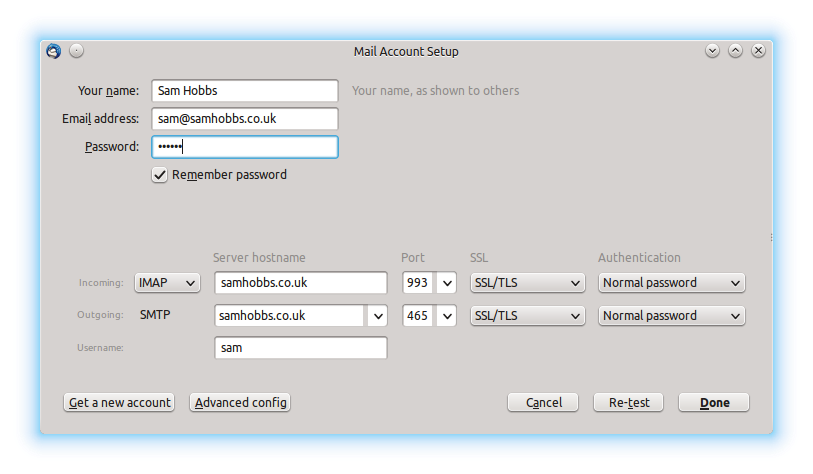 Now try emailing yourself from your external email address, and see if your email gets through. If you are having problems, be sure to check you’ve set up an MX record as well as a DNS A record.
Now try emailing yourself from your external email address, and see if your email gets through. If you are having problems, be sure to check you’ve set up an MX record as well as a DNS A record.
Stuck in spam filters?
A few people have contacted me recently to say that their email server is working fine but their emails are getting sent to Gmail's spam folder. If you are experiencing problems like this (or even if you're not), try setting up an SPF and/or PTR record as explained in my DNS basics tutorial. You might also want to check if your domain name or IP address are on any blacklists. There's a handy website called MX toolbox that lets you do this (choose blacklist check from the dropdown menu).
Almost done…
Good news! If you’ve reached this far and everything is working, then you’re almost done. The next step (Webmail with Squirrelmail) is optional but by far the easiest of the three steps. If you’ve hit a rut, please post a comment and I’ll try and help you out. If not… continue to Raspberry Pi Email Server Part 3: Squirrelmail
Comments
Lol.
Ouch...
Hi Sam
Sometimes a reboot helps ;) And now I have systemctl available either :)
I used that time the "standard installation" - instead of minimum installation - and got rid of anything what I don't need.
That time smtps comes up without restarting it at reboot.
Do you know how I can fix that (and where's the server log???):
Now I try to get fetchmail running. It just doesn't run.
Anyway: thanks for your help and have a lovely Christmas :)
(You can help me with my fetchmail, if you like ;) )
Testing SASL
Hello, Im at "Testing SASL" and write telnet localhost 25 in the terminal but only got a
"Trying ::1...
Trying 127.0.0.1...
telnet: Unable to connect to remote host: Connection refused"
Check if postfix is running
/var/log/mail.err)? SamError log: "fatal: no SASL
Error log: "fatal: no SASL authentication mechanisms"
SASL is provided by Dovecot.
postfix is active (running)
postfix is active (running)
Can't get mail to postmaster
I set up mail system on mx RPi2 Raspbian Jessie according to your instruction. As far as I can see, things are working OK. However I have an issue. I cannot get postmaster@ to receive mails. Logs mail.err and mail.warn are empty. Mail client I am sending from shows no errors and gets no return mails. I've spent couple of hours trying to find whats going on and I am nowhere closer to solution. I'd appreciate any suggestion you might have how can I troubleshoot this thing.
Regards, Vladimir
aliases
/etc/aliases) and then runsudo newaliases? SamAliases
I never even viewed or touched /etc/aliases. But on your suggestion I went and checked: there was a line saying: postmaster: root. I commented the line out, run newaliases as you suggested and now mail to postmaster works as expected. I guess it was set so either on Raspbian jessie distrib or by installing one of the mail packages ?!?
Anyway the trouble is gone! I must say your tutorial on installing the mail system is fantastic. I am practically a newbie on anything Linux and with help of your instructions I managed to do an install with very few glitches (mostly typos) on a first try! Now I have to read few (actually a lot of) things to gain better understanding what in fact I was doing :), especially thing about certificates,,,
Many thanks for your effort and help.
Since it is that time of the year:
Merry Christmas an Happy New Year, Vladimir
Great! Congrats, I hope it
Can't connect with user Pi
Hello Sam,
Thanks a lot for your efforts and for this great and thorough tutorial.
I am stuck with a weird problem, when trying to login (either via telnet or via the "openssl s_client -connect localhost:993 -quiet" command
if I try to login using a test user , everything goes perfectly but when I tried using the "pi" user (it doesn't hold the name Pi for me but another one, anyway I don't think it really matters) there's no way to login, I get the following:
"a NO [AUTHENTICATIONFAILED] Authentication failed."
looking in the mail log I have:"
dovecot: auth-worker(5241): Error: passwd-file: open(/etc/dovecot/users) failed: No such file or directory" and that as well:
Dec 18 15:42:33 dovecot: auth: Error: passwd-file(,127.0.0.1,): stat(/etc/dovecot/users) failed: No such file or directory
Any idea?
Thanks in advance for your answer and your time
With Kind Regards
Alain
Hi Alain,
/etc/dovecot/conf.d/auth-passwdfile.conf, which must have been included in/etc/dovecot/10-auth.confnear the bottom. You should have a section that looks something like this: The only line that should be uncommented is the one that includes auth-system. If you comment the rest you shouldn't see that error any more. A lot of these problems are due to the tutorial being written for Wheezy - some of the packaging defaults have changed in Jessie. Meanwhile, my server is still running Ubuntu 14.04, which is similar to Wheezy, so I haven't ever set it up "the Jessie way" and I'm troubleshooting for people as they find problems. Thanks for making it easy by providing a clear explanation of the problems you've been having! SamHi Sam,
Hi Sam,
Thanks for taking some time helping me figuring out this.
I looked at the
/etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conffile and it is as you mentioned: the"!include auth-system.conf.ext"line is uncommented.And my
/etc/dovecot/conf.d/auth-passwdfile.conf.extfile looks like this:# Authentication for passwd-file users. Included from 10-auth.conf.
#
# passwd-like file with specified location.
#
passdb {
driver = passwd-file
args = scheme=CRYPT username_format=%u /etc/dovecot/users
}
userdb {
driver = passwd-file
args = username_format=%u /etc/dovecot/users
# Default fields that can be overridden by passwd-file
#default_fields = quota_rule=*:storage=1G
# Override fields from passwd-file
#override_fields = home=/home/virtual/%u
}
I've tried searching for similar problems on line but no success yet.
What I am going to do: changing the test account password and make it longer and with some random characters as per my user one and see how it goes... I'll let you know then.
Thanks again for your time
Oh, and no worries for not answering straight away as, first, I didn't expected it at all, and second I was myself off my computer after sending my message.
Kind Regards
Alain
Hey Sam,
Hey Sam,
Just a feedback from my tests. So no matter how complicated and long the password is for the test account, I can login successfully. And to the opposite, definitely no success with my user account. That's really weird.
I wonder what I've done wrong or missed when doing the settings...
I'm going to do more researches... :)
Have a nice day
Kind Regards
Alain
Some more details about my problem...
Hello Sam,
I just realised I forgot to mention something that might be important: the issue about not being to log in with my pi user account started at the testing SASL part of your tutorial (it works seamlessly with the testing account though).
Can it be related to the length and "complexity" of the password I am using for my user account? Or something going wrong during the base64 encoding of login and password?
I am going to try testing that following this: http://wiki2.dovecot.org/Debugging/Authentication and see how it goes.
Kind Regards
Alain
Error when sending mail from external address
Thanks for this tutorial! All went well with no single glitch until the very last step: when sending an email from an external address, the message bounced back with an "550 5.1.1 <...>: Recipient address rejected: User unknown in local recipient table." What could this be?
I figured it out
Hey -- I figured it out; please discard my comments. Thanks again for the tutorial -- incredibly well done!
Emails rejected
First of all, thanks for this tutorial. Sadly, I'm having some issues. Here is a log snippet which will propably help find the cause:
connect from unknown[209.85.215.44]Postfix/smtpd [771]:NOQUEUE: reject: RCPT from unknown[209.85.215.44]: 450 4.7.1 : Helo commmand rejected: Host not found; from= to= proto=ESMTP helo=
disconnect from unknown [209.85.215.44]
Check helo restrictions
permit_sasl_authenticatedbeforereject_unknown_helo_hostname. If you had that in the list, it would allow any helo hostname when the email client authenticates before sending an email because the permit part is closer to the start of the list. Your helo restrictions should look like this:smtpd_helo_restrictions = permit_mynetworks, permit_sasl_authenticated, reject_invalid_helo_hostname, reject_non_fqdn_helo_hostname, reject_unknown_helo_hostnameSamFirst of all,sorry but the IP
First of all,sorry but the IP addresses disappeared. Anyways my server can send emails perfectly, but it refuses to recieve them. I'll try putting a new log snippet here:
postfix/smtpd[770] connect from unknown[74.125.82.53]
postfix/smtpd[770] NOQUEUE: reject: RCPT from unknown[74.125.82.53]: 450 4.7.1 (mail-wm0-f53.google.com): Helo commmand rejected: host not found:from=redacted@Gmail.com to=example@example.com proto=ESMTP helo=(mail-wm0-f53.Google.com)
Postfix/smtpd[770] disconnect from unknown[74.125.82.53]
check dns resolution
Hi Sam,
Your test gave the same answer
SSL Certificates
Sam,
Thank you for the Tutorials which I have read an actioned with great success.
BUT.... I have messed around with the ssl certificates to the point that I cannot send or receive e-mails on my home server.
I'm running a raspberry Pi 2 with the standard wheezy OS.
Can you briefly explain how to restore a working certificate?
Regards Richard
Difficult to say without
Dovecot won't start
Hi Sam - Great tutorials and I was going along fine. I'm using a RaspberryPi Mk2. Section 1 - postfix - is all OK and I was able to send emails to myself using telnet. I followed section 2 - dovecot - to the point where you ask for the postfix and dovecot services to be restarted, as in:-
Now restart Postfix and Dovecot:
sudo service postfix restart
sudo service dovecot restart
We’re now going to try and send an email after authenticating with SASL.
But I get a failure on dovecot restarting. It says 'Job for dovecot.service failed'. I look at the status and I get:
dovecot.service - LSB: Dovecot init script
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/dovecot)
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Sun 2016-01-10 15:18:51 AWST; 7min ago
Process: 2169 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/dovecot start (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
and that's where I'm stuck! I have gone back over the instructions on the two sections up to this point and double checked all the conf files etc you have modified. I can't see a mistake - any ides what is wrong??
Thanks so much for a great tutorial and any help you can give.
Mike
What's in the log?
/var/log/mail.errfor anything relevant. I don't think the Dovecot common/core is significant, it's probably just a packaging change between Wheezy and Jessie. SamMail.err
Thanks so much for answering, Sam. I have removed both Postfix and Dovecot and started from scratch again. I'm at the end of page 1 and all works exactly as expected. I'll move on to page 2 (Dovecot) tomorrow (it's late here in Perth!). BTW, if I 'sudo service dovecot restart' at the moment (with no changes made), it works. Looked in the mail error log and it says:
Jan 10 15:55:03 raspberrypi2 postfix/smtpd[1844]: fatal: no SASL authentication$
multiple times. That seems to be a clue? I'll work through commands tomorrow and see how it goes.
Kind regards
Mike
Cool, let me know if you have
Add new comment